Advertisement
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| public TextArea() | Creates a new TextArea.. |
| public TextArea(String text) | Creates a new TextArea with specified text. |
| public TextArea(int rows, int columns) | Creates a new TextArea with specified number of rows and columns. |
| public TextArea(String text, int rows, int columns) | Creates a new TextArea with a text and a number of rows and columns. |
| Methods | Description | public void setText(String text) | Sets a String message on the TextArea. |
|---|---|
| public String getText() | Gets a String message of TextArea. |
| public void append(String text) | Appends the text to the TextArea. |
| public int getRows() | Gets the total number of rows in TextArea. |
| public int getColumns() | Gets the total number of columns in TextArea. |
import java.awt.*;
public class TextAreaEx1
{
Frame jf;
TextArea textArea1, textArea2, textArea3, textArea4;
TextAreaEx1()
{
jf= new Frame("TextArea");
textArea1 = new TextArea(); //TextArea()
textArea2 = new TextArea(2,2); //TextArea(int rows, int columns)
textArea3 = new TextArea("Third textarea", 10,10);
textArea4 = new TextArea("Fourth textarea", 5,20);
textArea1.append("First textarea");
textArea2.append("Second textarea");
jf.add(textArea1);
jf.add(textArea2);
jf.add(textArea3);
jf.add(textArea4);
jf.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
jf.setSize(500,400);
jf.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String... ar)
{
new TextAreaEx1();
}
}
 Figure 1
Figure 1 Advertisement
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class TextAreaEx2 implements ActionListener
{
Frame jf;
TextArea textArea1;
Label label1, label2;
Button button;
TextAreaEx2()
{
jf= new Frame("TextArea");
label1 = new Label("Please mention your favorite fruits in the textbox");
button = new Button("Submit");
label2 = new Label();
textArea1 = new TextArea(5,45);
jf.add(label1);
jf.add(textArea1);
jf.add(button);
jf.add(label2);
button.addActionListener(this);
jf.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
jf.setSize(375,250);
jf.setVisible(true);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae)
{
if(ae.getActionCommand().equals("Submit"))
{
label2.setText(" Your favorite fruits - " + textArea1.getText());
jf.setVisible(true);
}
}
public static void main(String... ar)
{
new TextAreaEx2();
}
}
When you run the code, you are presented a window shown in the Figure2. In this window you are asked to enter your hobbies in the textbox -:
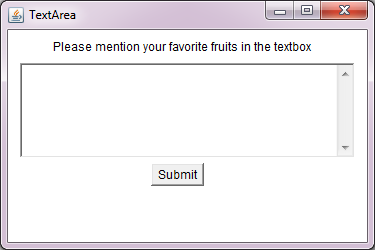 Figure 2
Figure 2 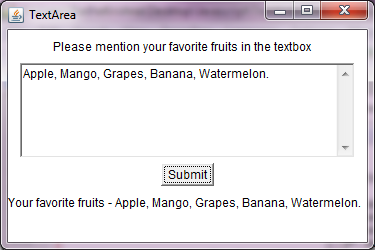 Figure3
Figure3
Advertisement
Advertisement
Please check our latest addition
C#, PYTHON and DJANGO
Advertisement