Advertisement
goto label;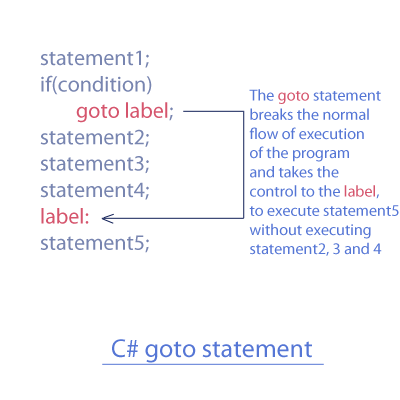
// C# The goto statement example
using System;
class A
{
public static void Main()
{
int age = 16;
if(age<21)
goto Under21Team;
else
Console.WriteLine("Welcome to Senior Team");
Console.WriteLine("All the best!");
Under21Team:
Console.WriteLine("We are sorry, you are too young to enter our Senior team");
}
}We are sorry, you are too young to enter our Senior teamAdvertisement
// C# The goto statement example
using System;
class A
{
public static void Main()
{
int age = 25;
if(age<21)
goto Under21Team;
else
Console.WriteLine("Welcome to Senior Team");
Console.WriteLine("Do Great!");
Under21Team:
Console.WriteLine("The program has ended");
}
}Welcome to Senior Team
Do Great!
The program has ended// C# goto statement to go out of the loop
using System;
class A
{
public static void Main()
{
int counter = 10;
while(counter>=0)
{
counter=counter-1;
Console.WriteLine("Counter : " + counter);
if(counter==4)
goto ExitingLoop;
}
ExitingLoop:
Console.WriteLine("We are out of the loop at the counter 4");
}
}Counter : 9
Counter : 8
Counter : 7
Counter : 6
Counter : 5
Counter : 4
We are out of the loop at the counter 4
Advertisement
Advertisement
Please check our latest addition
C#, PYTHON and DJANGO
Advertisement